In an email sent on October 31, 2008, Satoshi stated, “I’ve been working on a new electronic cash system that’s fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party.”
It has been 15 years since Oct. 31, 2008, often known as Halloween, when the anonymous creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, sent the white paper to a mailing list of cryptographers.
In the famous first line, Satoshi stated, “I’ve been working on a new electronic cash system that’s fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party,” before providing a link to the paper, “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”

A decentralized system that might enable peer-to-peer transactions was suggested in the white paper as a potential solution to the “double spending” issue that is frequently connected to digital money.
Launched barely two months later on January 3, 2009, it promised to do this via a network of nodes to validate and record transactions through a proof-of-work consensus process.
How The Bitcoin Project Came To Be
Satoshi’s breakthrough in computer science was preceded by other noteworthy advancements in the fields of e-money and encryption.
Wei Dai’s creation of B-money, an electronic peer-to-peer payment system that never went live but was crucial to Satoshi Nakamoto’s ideas for Bitcoin, is the first source mentioned in the Bitcoin white paper.
Similar to Bitcoin, B-money suggested that users of the system keep track of who owns money in a database of account balances. A broadcast message to all participants would commence and finish transactions, updating the account balances of individuals participating in a particular transaction.
It may be viewed as somewhat of a forerunner to the Bitcoin protocol’s nodes, which maintain a log of the ever-expanding blockchain.
evidence-of-work, a type of cryptographic evidence in which one party certifies to others that a particular amount of a particular computational effort has been performed, is necessary for this procedure.
By referencing Adam Back’s 1997 creation of Hashcash, which used proof-of-work to prevent denial-of-service assaults and email spam, Satoshi integrated this into Bitcoin.
Another essential component of Bitcoin that Satoshi successfully developed is timestamps.
When a block of transactions is added to the blockchain of Bitcoin, the timestamp server for that block is activated by taking a hash of that block, which is similar to a unique serial number.
The hashes preserve the integrity of the Bitcoin data by cryptographically connecting one block to the next. Additionally, timestamps on Bitcoin prevent double spending, making the network unchangeable and impervious to tampering.
Henri Massias, Scott Stornetta, Stuart Haber, and Dave Bayer’s contribution was acknowledged by Satoshi when he included timestamping into the Bitcoin protocol.
In the meanwhile, Bitcoin now uses Merkle trees to validate transaction data using digital signatures. Ralph Merkle’s work on creating public-key cryptosystems was mentioned by Satoshi.
Cyperphunk and Bitcoin supporter Jameson Lopp earlier stated to Cointelegraph that recognition need to go to the early initiatives that helped create the platform for Bitcoin.
But according to Lopp, Satoshi’s genius was in his ability to patch together all these parts into a working system:
“In my opinion, no single component of the puzzle is more crucial than the others. The subtle way that each component of Bitcoin interacts with the others to give the system life is what makes Nakamoto so brilliant, not any of the individual parts.
How Bitcoin Was Operated
One of the first products to successfully employ encryption to keep money independent from the state at the time was Bitcoin. Thanks to Satoshi’s creation, people could transact with others all over the world without having to go through banks or other financial organizations.
When Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 BTC for two pizzas in May 2010, it was the first real-world transaction made with Bitcoin.
In the beginning, the media emphasized that criminals were using Bitcoin more frequently to launder money, among other things, but that story has since changed.
All throughout the world, its adoption is growing. September 2021 saw its legal tender status in El Salvador.
Recently, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for spot Bitcoin have been made available by financial institutions in the US, and other institutions have started offering Bitcoin ETFs in Europe.
A number of changes have been made to help Bitcoin grow and expand its network of applications.
In 2018, the Lightning network was introduced with the goal of accelerating Bitcoin transactions using off-chain computing.
Ordinals are a type of nonfungible token that were introduced on Bitcoin in January. The Taproot soft fork in November 2021 allowed for its debut.
The price of bitcoin has also fluctuated greatly.
BTC began trading for as little as a cent in 2009 and has since gone through many boom and bust cycles, with price swings of up to 88% at times.
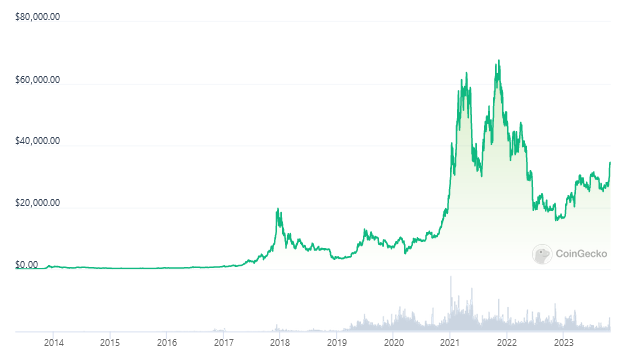
As of this now, the price of Bitcoin is $34,350, which is 50% less than its peak price of $69,000 on November 10, 2021.































