Do you yet understand the terms nodes, miners, protocols, and mempools? We understand that beginning your cryptocurrency adventure might be very overwhelming. If you are interested in learning more about cryptocurrency, regardless of whether you are a total newbie, crypto-curious, or have a basic idea of how things operate, you have come to the correct spot. It may be difficult to know where to start and can frequently feel like a foreign language. Similar to learning a new language, once you master the essential vocabulary, everything else just flows from there. So let’s examine the terminology used in the transaction process, how it works, and what it implies for people like you and me.
What is the Blockchain?
Blockchain is really just a huge, automated, decentralized ledger (or database). The main goal of cryptocurrency is to establish a digital currency that enables peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions without the intervention of a third party. The blockchain allows for the safe transmission of a wide range of assets, including contracts, real estate, money, and more, without the need for a middleman like a bank or government.
What exactly is a blockchain transaction?
On the blockchain, a transaction is a value transfer. A transaction is, to put it simply, when one person transfers a certain quantity of bitcoin they hold to another person.
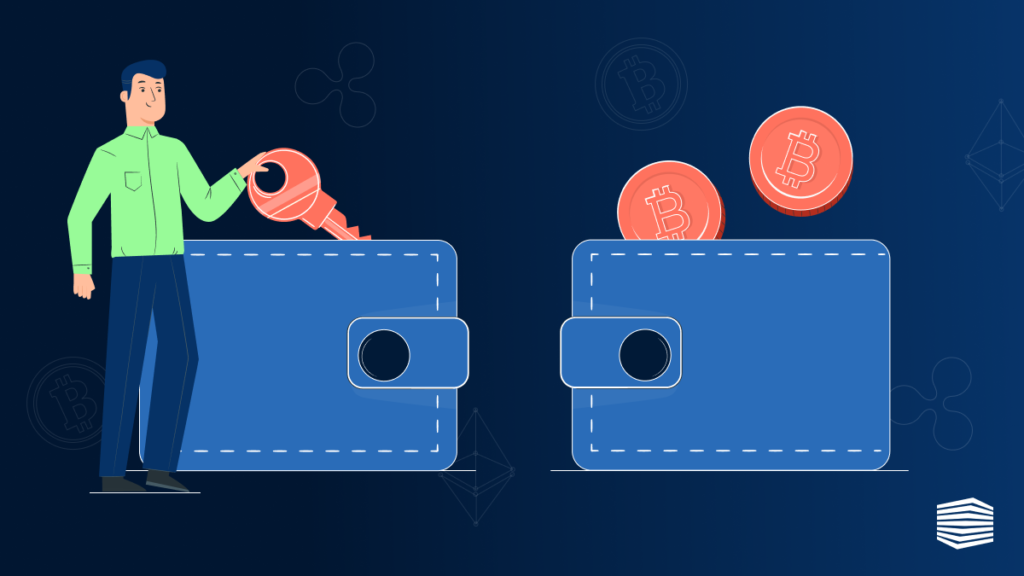
You need a wallet to conduct transactions on the blockchain. A wallet is a private application connected to the blockchain that manages your cryptocurrency holdings and enables you to conduct transactions using it. Each wallet is secured by a unique cryptographic technique that employs a private and public key pair that are separate yet related.
An individual must reveal their public key, commonly referred to as their address, in order to receive money. A private key, on the other hand, permits the expenditure of any monies received by the associated public key, therefore it must be kept hidden, much like your bank card pin number.
A user (whoever has the private key) can approve or sign transactions using their wallet, which allows them to transfer money to a new owner. The blockchain then adds the transaction when it is broadcast to the network.
A Transaction’s Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let’s begin by presenting the players involved in a transaction before getting into the specifics.
First, there are the users, which are individuals like you and me who wish to conduct a transaction using the blockchain’s functionalities. But who actually makes it happen in a society without a centralized structure?
Miners step in at this point. We are aware that the blockchain is a trustless system, one that enables users to be confident that their transaction will be honored accurately in the absence of a centralized authority. This is made feasible by miners by verifying incoming transaction blocks, which are collections of requested transactions that are awaiting confirmation in the mempool before being added to the blockchain. The incentive that keeps the system going is the payout that the miner or miners receive for successfully completing the task. Ever questioned why we pay for gas? Here’s your response: they help offset the energy costs associated with mining transactions and contribute to the block reward for miners.
The nodes are the last thing we have. Even you and I are capable of acting as nodes. By approving the transaction blocks supplied by the miners before they are added to the blockchain, nodes maintain the integrity of the whole system. To make sure everything matches, they accomplish this by comparing the incoming data with the blockchain’s transaction history. The network nodes, which are dispersed over the earth, must then agree as a group that new transactions are legitimate before adding them to the blockchain.
A transaction’s procedure may be divided into six steps:
- Someone makes a transaction request. The exchange might be made using cryptocurrencies, contracts, documents, or other data.
- All P2P participating computers in the relevant blockchain network are broadcasted the transaction. Nodes are what they are. Every transaction is published to the memory pool, often known as the mem-pool, where it is regarded as “pending.” In order to cover the cost of the computational power needed to execute and validate transactions on the blockchain, gas fees are added by users as part of the transaction.
- It is verified by miners. Every computer in the network compares the transaction against a set of validation standards that the designers of the particular blockchain network have established.
- Validated transactions are kept in blocks that are secured with locks called hashes.
- The current Blockchain receives a brand-new block. When other computers in the network verify that the lock on the block is accurate, this block is added to the blockchain.
- The deal has been concluded. Since the transaction is now a part of the blockchain, it can no longer be changed.
Networks Can Agree in a Variety of Ways
How to validate transactions without a centralized authority is one of the obstacles in building a crypto network, and to do so, you need people—lots of people! Also, in order to demonstrate their willingness to witness to a transaction’s authenticity, participants need an incentive, which is typically some local cash.
There are now two ways to certify Proof-of-Work (PoW), where the energy and computational resources used to solve difficult mathematical problems are at risk. It is effectively a competition amongst miners since when they are the first to solve the equation, they receive the prizes.
Stakers, the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model’s version of miners, secure money in a smart contract. Every time the network requires a new block, an algorithm gives a certain staker the chance to publish the following block. Based on each staker’s share of the total amounts staked, the algorithm chooses the staker through a lottery.
While a few other cryptocurrencies like Tezos and Cosmos employ PoS as an alternate consensus method to Bitcoin’s PoW consensus, PoS is becoming more popular. PoW to PoS conversion is also happening with Ethereum. PoS was developed in order to deliver the network quicker transaction speeds, improved scalability, and decreased energy usage while eliminating the enormous energy cost.